
This page last revised 23 August 2006 -- S.M.Gon III
Introduction
Ecoregion
Conservation Targets
Viability
Goals
Portfolio
TNC Action Sites
Threats
Strategies
Acknowledgements
▫
Tables
Maps & Figures
CPT Database
Appendices
Glossary
Sources
.


Wiliwili (Erythrina sandwichensis) is a summer-deciduous tree and a dominant canopy species of lowland dry forest.
Lowland Dry System
Natural communities below1,000 m (ca 3,000 ft) elevation, receiving less than50 inches annual precipitation, or otherwise bearing prevailinglydry substrate conditions comprise the lowland dry system in theHawaiian High Islands Ecoregion. This system is found on theislands of Hawai‘i, Moloka‘i, Lāna‘i,Kaho‘olawe, O‘ahu, and Kaua‘i, and is best developedon the leeward sides of the islands, for example, the Kona flankof Mauna Loa, the leeward flank of West Maui, the leeward side ofEast Moloka‘i, the north slopes Lāna‘i andKaho‘olawe, the lower slopes of the Wai‘anae Mountains(O‘ahu), and the leeward slopes of Kaua‘i. It occurstypically below the lowland mesic system. There are a number of naturalcommunities described within this system, including a variety of grasslands, shrublands, and forests. Biologicaldiversity is low to moderate in this system, and specialized plants and animals occur there, such as pueo, the Hawaiian owl (Asio flammeus sandwichensis) and the rare Hawaiian tree cotton, hau hele ‘ula (Kokia spp.)

Many plants of the lowland dry system, such as this endemic tree cotton Kokia drynarioides are rare and endangered, threatened by loss of habitat, wildfire, feral ungulates, and invasive weeds.
Natural communities and species of this system are listed among nested targets via the appendices.

The distribution of the Lowland Dry System across the Hawaiian High Islands Ecoregion is depicted below:
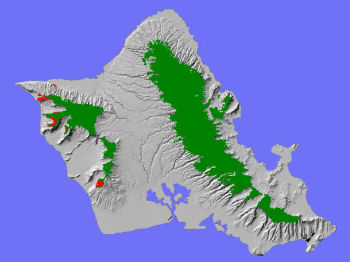
TheLowland Dry System on O'ahu (red areas above) has been reduced byfire, weeds, and feral ungulates to small remnants on the leewardslopes of the Wai'anae conservation area.
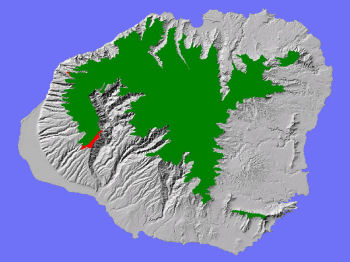
TheLowland Dry System on Kaua'i (red areas above) has been reduced byfire, weeds, and feral ungulates to small remnants on the leewardslopes of the conservation area.


Natural communities and species of this system are listed among nested targets via the appendices.

The distribution of the Lowland Dry System across the Hawaiian High Islands Ecoregion is depicted below:



The Lowland Dry System in Hawai‘i includes a variety of grasslands, shrublands and woodlands, typically on leeward slopes.

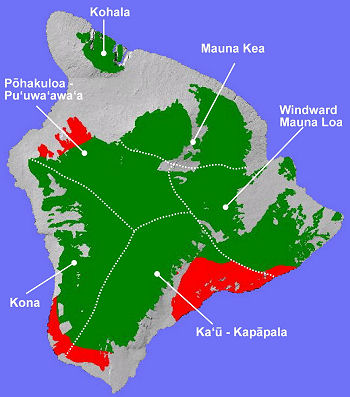
The Lowland Dry System on Hawai‘i Island(red outlined shaded areas above) occurs in four conservation areas (Windward Mauna Loa, Ka‘ū-Kapāpala, Kona, and Pōhakuloa-Pu‘u Wa‘awa‘a).
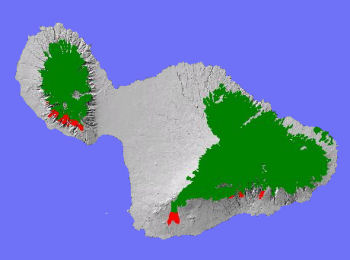
TheLowland Dry System on Maui (red areas above) occursbelow 3,000 feet elevation, on the leeward slopes of both East Maui andWest Maui conservation areas.
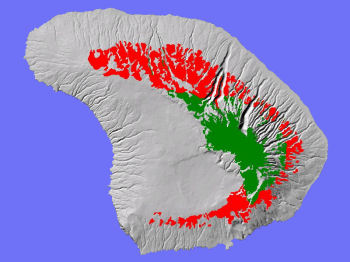
TheLowland Dry System on Lāna'i (red areas above) occursbelow 3,000 feet elevation, and despite good size, is heavilyfragmented, and has been degraded by fire, feral ungulates, and weedinvasions.
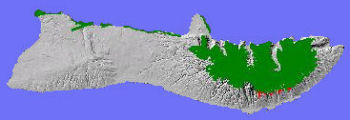
TheLowland Dry System on Moloka'i (red areas above) has been reduced byfire, weeds, and feral ungulates to small remnants on the leewardslopes of the East Moloka'i conservation area.

